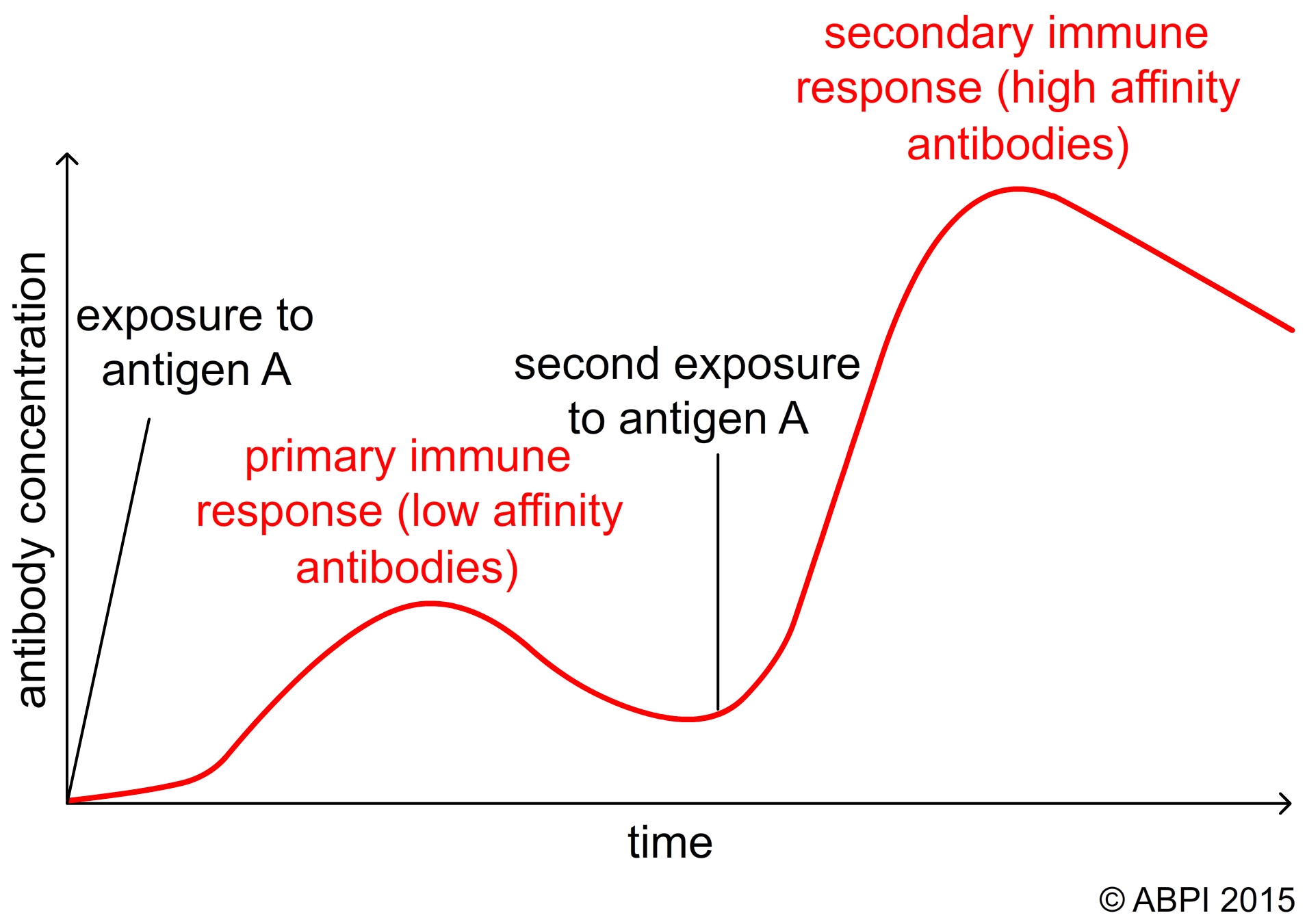
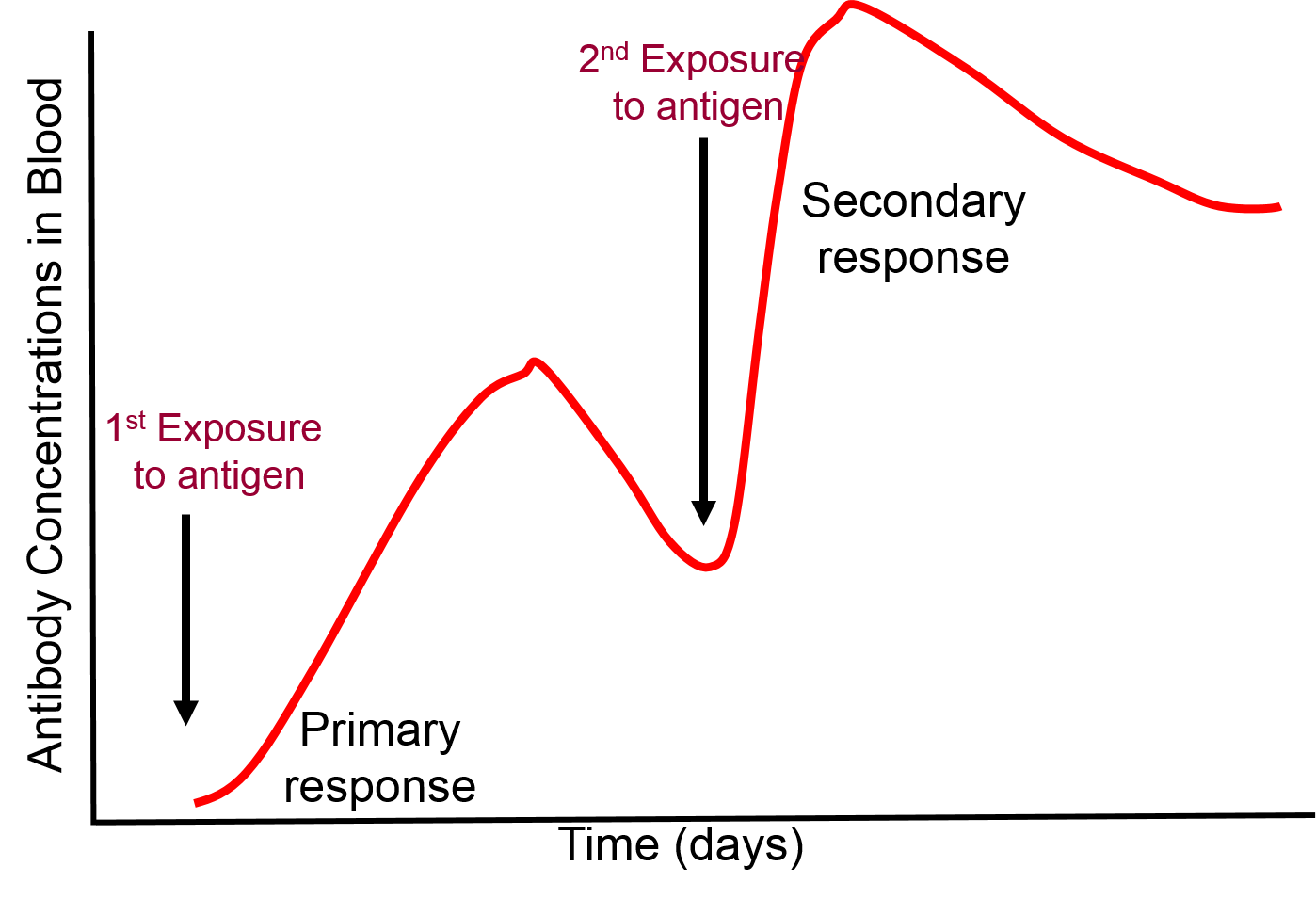
Which types will lead to long lasting immune. 2 Any compromise in immune function unrelated to inherited defects in the immune system.
Immunity can either be natural or artificial.

. The magnitude of the lymphocyte transformation reaction was higher in the naturally infected than in the. Artificial Passive Immunity. Providing instant protection is the main advantage of passive immunity whereas active immunity takes time to develop typically several weeks.
This is when ready-made antibodies from another source are introduced to the body. Exposure to an infection or disease. Antibodies are proteins produced by the body to neutralize or destroy toxins or disease-carrying organisms.
1 Any immune response to exogenous antigens. It can be either naturally or artificially acquired. It is when the antibodies required to kill an infection are introduced directly into the body.
Usually this happens through an injection of antibodies. On the other hand passive. Natural and artificial immunity 10.
Provide artificial active immunity. Artificially acquired active immunity is protection produced by intentional exposure of a person to antigens in a vaccine. Acquired or adaptive immunity can be divided in to Natural Active Natural Passive Artificial Active and Artificial Passive Immunity.
Another persons antibodies infection-fighting. Also they can be active and passive. The vaccine also an immunogen helps to induce artificial active immunity.
Passive immunity is defined as a particular antigen resistance provided by external antibodies. The vaccine is a mixture of an antigen that helps to generate immune response artificially. A prominent difference between active and passive immunity is that active immunity is developed due to the production of antibodies in ones own body while passive immunity is.
Artificial induction of immunity is immunization achieved by human efforts in preventive healthcare as opposed to and augmenting natural immunity as produced by organisms. Lets explore what active immunity and passive immunity are. 3 Immunity in which.
Immunity is the ability of a body to guard itself against diseases. One vaccinated subject had VZV-specific IgA and IgM in the serum. In artificial passive immunization there is no involvement of the.
For example measles antibody will protect a. It can come from. Types of Specific Immunity Naturally acquired active immunity type of specific immunity a host develops after.
Acquired immunity is immunity you develop over your lifetime.
11 1 Defence Against Infectious Disease Bioninja
11 9 5c The Role Of Circulatory System In Body Defence Mechanism Objective Questions Spm Biology

Defense Against Disease Active And Passive Immunity Plantlet
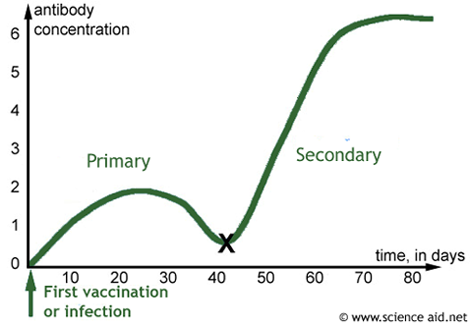
Vaccination And Immunity Immunological Memory Vaccination Passive Immunity Scienceaid
11 9 5c The Role Of Circulatory System In Body Defence Mechanism Objective Questions Spm Biology

Nota Latihan Biology Kssm Form 4 Bab 11 3 Weacademia 2021

Nota Latihan Biology Kssm Form 4 Bab 11 3 Weacademia 2021

The Times Of India On Twitter Uk Approval Of Oxford Astrazeneca Covid19 Vaccine Positive News Waiting For India S Approval Serum Institute Read Https T Co R3381bvbqu Https T Co Pxwellcn2l Twitter

Immunity First And Second Dose Of Injection With Graph Pdf
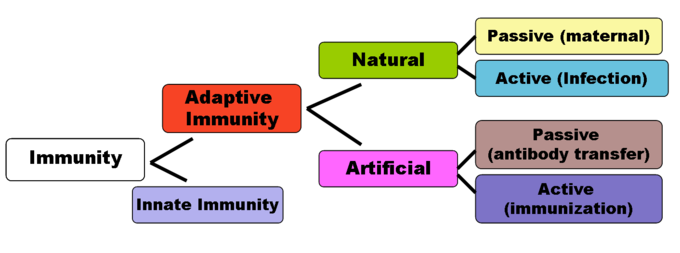
11 12c Artificial Immunity Biology Libretexts
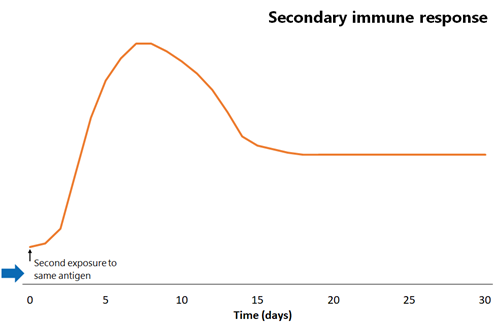
1 General Immunisation Principles Immunisation Handbook 2020 Ministry Of Health Nz

F4 Chapter 11 Immunity In Humans Biology Quizizz
11 9 5a The Role Of Circulatory System In Body Defence Mechanism Objective Questions Spm Biology
Artificial Passive Immunity Graph Randytrf
Summative Practice 11 Question 4 Form 4 Biology Textbook Exercise And Answer Spm Biology

The Adaptive Immune Response B Lymphocytes And Antibodies Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Immune Defense Against Bacterial Pathogens Adaptive Or Acquired Immunity